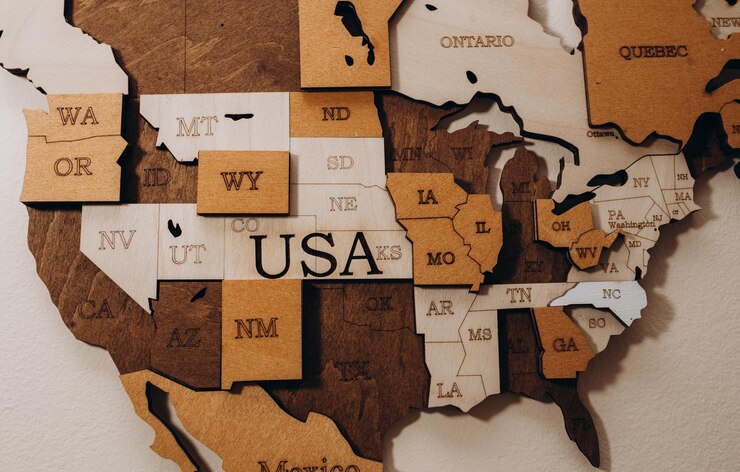
The Map of the US is more than just a visual representation of states and boundaries. It’s a powerful tool that reflects the country’s rich geography, diverse cultures, and historical evolution. Whether you’re a student, traveler, or just curious, diving into the map of the United States opens up a world of fascinating details about its landscapes, climate zones, and regional characteristics.
From the rolling plains of the Midwest to the towering Rocky Mountains and the sun-soaked coasts of Florida and California, the US map helps explain how geography influences everything, from culture to economic activity. Let’s take an in-depth look into the layout of the United States and what makes its map so interesting.
The Map of the US: A First Glance
At first glance, the map of the US is a patchwork of 50 individual states, each with its own borders, capitals, and cities. The contiguous United States consists of 48 states in mainland North America, with Alaska located in the far northwest and Hawaii situated in the Pacific Ocean. But this basic understanding of the US map hides the intricacies of its natural features, political divisions, and diverse regions.
A map of the US often includes more than just state boundaries. Rivers, mountain ranges, and major cities are key landmarks that further define the country’s landscape. These features also reveal how history has shaped the country’s development, especially in terms of population distribution and economic activities.
Understanding the Geographic Regions of the US

The geographic regions of the US can be broken down into several major areas, each with its own unique features:
- Northeast: Known for its bustling cities like New York and Boston, the Northeast is a hub of political, economic, and cultural activity. Its map features densely populated urban areas and significant historical landmarks.
- Midwest: The Midwest, often called America’s “heartland,” is dominated by vast plains and agricultural areas. Major cities such as Chicago are marked on the map, surrounded by agricultural hubs that have historically supported the country’s food supply.
- South: Stretching from the Atlantic coastline through the Gulf of Mexico, the Southern states are marked by warm climates, a rich cultural history, and diverse landscapes, including the Appalachian Mountains.
- West: The West is perhaps the most geographically varied region, from the deserts of Arizona to the forested peaks of the Rockies and the iconic Pacific Coast. California and Nevada offer stark contrasts in terms of geography, showing the dynamic range on the US map.
These regional distinctions are not just for understanding geography. They influence local economies, population trends, and even political ideologies.
Rivers, Lakes, and Other Key Features on the US Map
When examining a map of the US, one can’t overlook the many natural features that have played a vital role in the country’s development. The Mississippi River, one of the longest rivers in the world, flows south through the heart of the country, defining many state boundaries along its course. The Great Lakes, located in the northern Midwest, form the largest group of freshwater lakes globally and are crucial for shipping and transportation.
- The Mississippi River: The backbone of US inland water transportation, this river is essential for understanding American trade routes and settlement patterns.
- The Great Lakes: Forming part of the US-Canada border, the Great Lakes (Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario) are key landmarks on any detailed map of the US.
- Rocky Mountains and Appalachian Mountains: Two of the most significant mountain ranges in the US, with the Rockies dominating the western map and the Appalachians stretching along the eastern part of the country.
Each of these features not only enhances the visual appeal of the map but also provides insight into how people have adapted to their environments across the country.
State Borders and Historical Changes on the US Map
The current borders on the map of the US reflect centuries of history, including land purchases, treaties, and statehood admissions. Originally consisting of just 13 colonies along the Atlantic coast, the US expanded westward in the 19th century through the Louisiana Purchase, the annexation of Texas, and the acquisition of California.
- Louisiana Purchase: This 1803 transaction between the US and France significantly enlarged the United States, adding vast territories that now comprise states like Louisiana, Missouri, and South Dakota.
- Texas and California: Both of these states joined the union under complex circumstances related to territorial disputes and wars, significantly altering the US map.
- Alaska and Hawaii: Added in the 20th century, these two states broadened the geographical boundaries of the United States and brought new natural resources and strategic importance.
The evolution of state borders is a testament to how political, economic, and social factors have continually shaped the nation.
Cultural and Economic Influence of US Geography
The map of the US also tells a story of how geography has influenced cultural and economic development. For example, the rich farmland of the Midwest has made it a leading agricultural region, while the natural harbors along the East and West Coasts have turned cities like New York, Los Angeles, and San Francisco into global trade centers.
- New England: Historically, the harsh winters and rocky soils of New England fostered industries like fishing, shipbuilding, and later, manufacturing.
- The South: Historically reliant on agriculture, the Southern US map shows states with warm climates ideal for growing crops like cotton, tobacco, and citrus fruits.
- West Coast: The region’s proximity to Asia has made it a major hub for trade and immigration, especially in cities like Los Angeles and Seattle, which are marked prominently on the US map.
These geographic factors have had long-lasting impacts, shaping the economic and cultural identities of various regions.
How the Map of the US Reflects Climate Diversity
The US is known for its climate diversity, and a map of the US gives a hint of how the climate shifts across the regions. The northern states, particularly those near the Canadian border, experience harsh winters, while the Southern states enjoy warmer, subtropical climates.
- Pacific Northwest: Characterized by a temperate, often rainy climate, this region is home to dense forests and sprawling mountain ranges.
- Southwest: The arid desert landscapes in states like Arizona and Nevada contrast sharply with the lush regions of the Southeast.
- Midwest: Known for its “four seasons,” the Midwest features everything from hot, humid summers to frigid, snowy winters.
These climate zones not only influence the daily lives of residents but also impact agriculture, tourism, and local economies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features to look for on the map of the US?
The key features to look for include state boundaries, major cities, rivers such as the Mississippi, the Great Lakes, and mountain ranges like the Rockies and Appalachians.
How does the US map influence state economies?
Geography significantly impacts state economies. For example, coastal states benefit from ports and trade, while agricultural states in the Midwest rely heavily on farming due to fertile land.
Why are some US state borders straight lines while others are more irregular?
Straight-line borders often result from political decisions, particularly in the west, where territories were drawn with fewer natural boundaries. In contrast, eastern borders were often influenced by rivers and mountains.
How did the Louisiana Purchase change the US map?
The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the US, adding vast territories west of the Mississippi River, leading to the creation of several new states and reshaping the nation’s geography.
Why do some parts of the US map show disputed territories?
Some areas on historical maps may show disputed territories, such as the Oregon Country, where the US and Britain had overlapping claims before final agreements were made.
What role do rivers play on the map of the US?
Rivers are crucial for transportation, agriculture, and setting state boundaries. The Mississippi River, in particular, has been vital to trade and the development of cities along its course.
Conclusion
The map of the US is a treasure trove of information, revealing not just geographical boundaries but also the rich cultural, historical, and economic stories of the country. From its major rivers and mountain ranges to its sprawling urban centers and rural landscapes, understanding the map of the United States offers a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of this vast nation. Whether you’re exploring for academic purposes, planning a trip, or simply curious about geography, the map of the US holds endless insights waiting to be uncovered