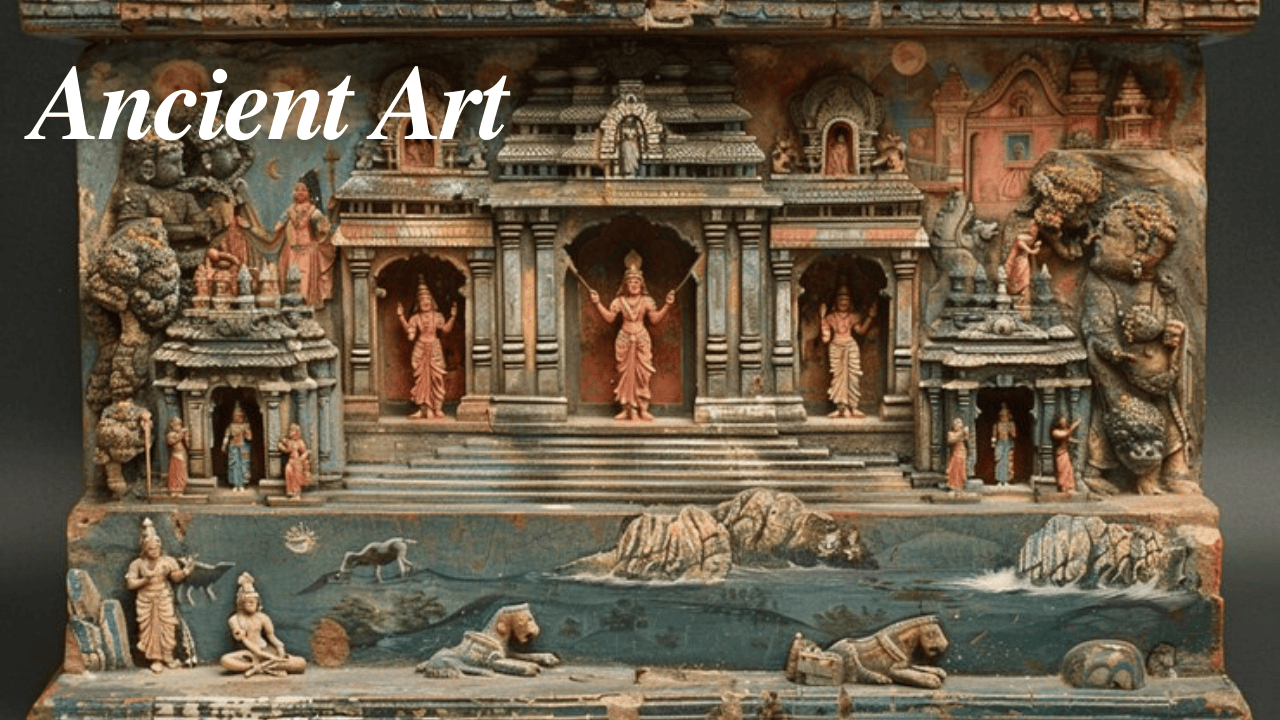
Ancient art stands as a testament to human creativity, cultural depth, and the symbolic language of early societies. For millennia, ancient artists across various civilizations used art as a means to record history, express spirituality, honor deities, and capture human experiences. From the captivating hieroglyphs of Egypt to the philosophical sculptures of Greece, each culture’s art provides unique insights into its values, beliefs, and aesthetics.
This article will dive into the mesmerizing world of ancient art, exploring its origins, techniques, materials, and symbolic meanings. Through a journey across major civilizations, we’ll look at how art shaped—and was shaped by—the historical context in which it thrived
Understanding Ancient Art?

Ancient art refers to the artistic created by early civilizations, ranging from the prehistoric era to the fall of the Roman Empire. This art often served as a visual language, narrating stories of gods, kings, battles, and rituals. Unlike modern art, which often prioritizes personal expression, ancient art typically carried communal or sacred significance, representing shared cultural values and beliefs.
The enduring appeal of ancient art lies in its intricate designs, carefully crafted techniques, and the symbolic meanings woven into each piece. From cave paintings to grand monuments, every artwork serves as a historical document, a bridge to understanding the cultures that shaped human civilization.
The Origins of Art
The earliest known forms of artistic expression date back to prehistoric times, around 30,000 BCE, with cave paintings found in regions such as Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc in France and the Bhimbetka caves in India. Early humans used natural pigments to depict animals, hunting scenes, and abstract patterns on cave walls, likely for ritualistic or storytelling purposes.
As societies developed, so did their art forms. Early art transitioned from simple carvings and paintings to elaborate sculptures, pottery, and architectural achievements. These artifacts marked the beginning of an era where art was not just functional but also symbolic, reflective of the community’s spiritual beliefs, and a means of preserving history.
Key Characteristics of Ancient Art
While ancient art varies significantly across cultures, certain traits are consistently found throughout:
- Symbolism: Much of ancient art used symbolism to convey religious and cultural beliefs.
- Functional Design: Often created with a purpose, whether ritualistic, ceremonial, or utilitarian.
- Natural Materials: Most ancient artists used locally available materials like stone, clay, and plant dyes.
- Focus on Spirituality and Nature: Ancient art often represented deities, animals, and natural elements, reflecting a deep connection to the spiritual and natural world.
Ancient Egyptian Art
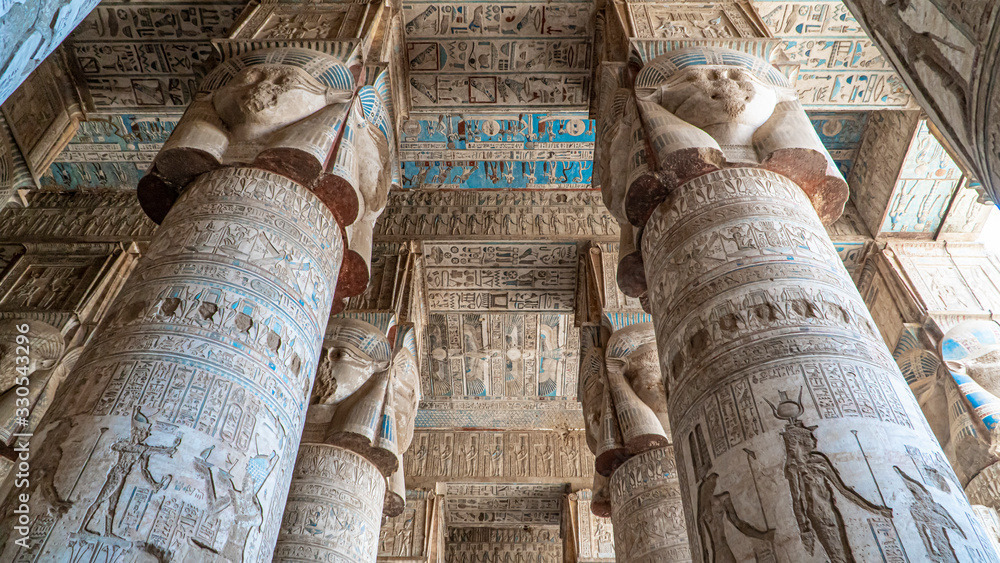
Ancient Egyptian art is among the most iconic in the world, renowned for its distinctive style and monumental architecture. Egyptian artists followed strict conventions, creating works that reflected balance, symmetry, and order. Their art primarily focused on the divine, the afterlife, and the majesty of pharaohs.
The Egyptians used hieroglyphics, a form of symbolic writing, to record events, prayers, and tales of the gods. Temples and tombs were adorned with carvings, paintings, and statues dedicated to gods and kings. Gold, lapis lazuli, and other precious materials often decorated Egyptian artifacts, symbolizing power, wealth, and eternity.
Symbolism in Egyptian Art
Egyptian art was filled with symbolic representations. The Ankh, a cross-like symbol with a loop at the top, represented life. The Eye of Horus was a protective symbol, while the scarab beetle symbolized rebirth and regeneration. These symbols were not merely decorative; they conveyed deep spiritual meaning and were believed to possess protective or empowering qualities for those depicted or entombed with them.
Ancient Mesopotamian Art
Mesopotamia, home to one of the world’s earliest civilizations, produced an art style focused on religious and royal themes. Artifacts from Mesopotamian culture include cuneiform-inscribed tablets, sculptures, and elaborate jewelry. Temples known as ziggurats were central to their architecture, reflecting the significance of religion in their society.
Ziggurat and Temple Art
Ziggurats served as temples, often dedicated to the gods who were believed to reside atop these towering structures. Mesopotamian art depicted scenes of divine worship, with figures offering tributes to gods or rulers. Reliefs on temple walls featured deities, mythological creatures, and scenes of court life, illustrating the society’s belief system and social hierarchy.
Ancient Greek Art
Ancient Greece introduced a transformative period in art history, celebrated for its realism, humanism, and idealized beauty. Greek artists sought to capture the ideal human form, emphasizing proportion, balance, and anatomical accuracy. This period saw the emergence of some of history’s most famous sculptures, including the Discobolus and Venus de Milo.
Sculpture in Greek Art
Greek sculpture developed from rigid, stylized forms to dynamic representations of human movement and emotion. Sculptures of gods, athletes, and historical figures became iconic symbols of Greek cultural values and its philosophical pursuit of beauty. Classical Greek sculpture, characterized by natural poses and detailed expressions, influenced Western art for centuries.
Ancient Roman Art
Roman art built upon Greek traditions but introduced innovations of its own, especially in the realms of portraiture and architecture. Romans valued realism in their art, often depicting individuals with specific, recognizable features. They adapted Greek art but focused more on storytelling and historical commemoration.
Roman Mosaics and Frescoes
Romans developed complex mosaics and frescoes to decorate floors and walls, creating colorful, intricate designs with small stones or tiles. These artworks illustrated scenes from mythology, everyday life, and nature, bringing beauty to public spaces and private homes.
Ancient Chinese Art
China’s ancient art forms centered around harmony, spirituality, and natural elements. Calligraphy became an essential art form, representing beauty and the power of the written word. Chinese art also included bronze sculptures, pottery, and painted scrolls, which depicted historical events, landscapes, and scenes of daily life.
Calligraphy in Ancient China
Chinese calligraphy is both an art form and a means of communication. Each stroke represents balance and harmony, echoing the Chinese belief in the interconnectedness of all things. Calligraphy was highly respected, and its practitioners were viewed as scholars who could channel a sense of spiritual insight through their brushwork.
Ancient Indian Art
Ancient Indian art is characterized by its spiritual focus, particularly in its representation of Hindu and Buddhist deities. Temples, sculptures, and paintings depicted gods, goddesses, and spiritual scenes. Artists often used stone and bronze to create intricate representations of divine figures.
Buddhist Art in Ancient India
In ancient India, Buddhist art flourished, particularly in the form of stupas and sculptures of the Buddha. These artworks were not only religious symbols but also tools for meditation and enlightenment. The Ajanta caves in Maharashtra showcase remarkable frescoes depicting the Buddha’s life, teaching, and the spiritual journey.
Art of the Americas
Ancient art in the Americas developed independently, with unique characteristics and symbols. Civilizations such as the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas created art that reflected their cosmology, religious beliefs, and social structures.
Mayan Art
Mayan art includes sculptures, pottery, and painted murals depicting gods, kings, and daily life. The Mayans also developed an advanced writing system, which was preserved on stelae, ceramics, and codices, recording historical events and astronomical knowledge.
Influence of Religion in Ancient Art
Across civilizations, ancient art was deeply influenced by religious beliefs. Deities, myths, and symbols of the afterlife permeated artworks, making them not just decorative objects but meaningful icons. This sacred quality of ancient art was essential, as it embodied the societies’ values, morals, and worldviews, preserving the spirit and identity of their cultures.
Techniques in Ancient Art
Ancient artists employed various techniques that have become foundational in art history. They used tools made from bones, stones, and metals, experimented with natural dyes, and carved elaborate designs into stone and wood. These materials and methods reflect the skill, creativity, and resourcefulness of early artists.
Impact of Ancient Art on Modern Art
The legacy of ancient art can be seen throughout history and into modern times. The balance, symmetry, and idealism of Greek and Roman art, for instance, continue to inspire Western art and architecture. Ancient techniques and symbols also find their way into contemporary design, affirming the timeless appeal of ancient aesthetics.
Frequently
What is ancient art?
Ancient art encompasses the artistic works created by early civilizations, often deeply connected to religious, social, and cultural beliefs.
What are some examples of ancient art?
Examples include Egyptian hieroglyphics, Greek sculptures, Roman mosaics, Mayan carvings, and Chinese calligraphy.
What techniques did ancient artists use?
Ancient artists used techniques like carving, painting with natural pigments, pottery, and frescoes, relying on tools made from natural materials.
Why was ancient art symbolic?
Ancient art often depicted spiritual beliefs, deities, and cosmological themes, making it symbolic and meaningful within each culture.
How did ancient art influence modern art?
Ancient art influenced modern art by providing foundational techniques, aesthetics, and themes that continue to inspire contemporary artists.
Which civilizations are famous for their ancient art?
Prominent ancient civilizations include Egypt, Mesopotamia, Greece, Rome, China, India, the Maya, and the Inca.
Conclusion
Ancient art serves as a window into the past, revealing the beauty, depth, and complexity of early human societies. Through their art, ancient civilizations have left us a legacy that continues to enrich our understanding of history, culture, and creativity. By studying these timeless creations, we connect with our ancestors and gain a deeper appreciation for the power of artistic expression across ages and cultures.